diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3572_maximize_ysum_by_picking_a_triplet_of_distinct_xvalues/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3572_maximize_ysum_by_picking_a_triplet_of_distinct_xvalues/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..64bbb8b4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3572_maximize_ysum_by_picking_a_triplet_of_distinct_xvalues/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3572_maximize_ysum_by_picking_a_triplet_of_distinct_xvalues
+
+// #Medium #Array #Hash_Table #Sorting #Greedy #Heap_Priority_Queue
+// #2025_06_10_Time_5_ms_(100.00%)_Space_82.11_MB_(56.00%)
+
+class Solution {
+ fun maxSumDistinctTriplet(x: IntArray, y: IntArray): Int {
+ var index = -1
+ var max = -1
+ var sum = 0
+ for (i in y.indices) {
+ if (y[i] > max) {
+ max = y[i]
+ index = i
+ }
+ }
+ sum += max
+ if (max == -1) {
+ return -1
+ }
+ var index2 = -1
+ max = -1
+ for (i in y.indices) {
+ if (y[i] > max && x[i] != x[index]) {
+ max = y[i]
+ index2 = i
+ }
+ }
+ sum += max
+ if (max == -1) {
+ return -1
+ }
+ max = -1
+ for (i in y.indices) {
+ if (y[i] > max && x[i] != x[index] && x[i] != x[index2]) {
+ max = y[i]
+ }
+ }
+ if (max == -1) {
+ return -1
+ }
+ sum += max
+ return sum
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3572_maximize_ysum_by_picking_a_triplet_of_distinct_xvalues/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3572_maximize_ysum_by_picking_a_triplet_of_distinct_xvalues/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..3c88dbe5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3572_maximize_ysum_by_picking_a_triplet_of_distinct_xvalues/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
+3572\. Maximize Y‑Sum by Picking a Triplet of Distinct X‑Values
+
+Medium
+
+You are given two integer arrays `x` and `y`, each of length `n`. You must choose three **distinct** indices `i`, `j`, and `k` such that:
+
+* `x[i] != x[j]`
+* `x[j] != x[k]`
+* `x[k] != x[i]`
+
+Your goal is to **maximize** the value of `y[i] + y[j] + y[k]` under these conditions. Return the **maximum** possible sum that can be obtained by choosing such a triplet of indices.
+
+If no such triplet exists, return -1.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** x = [1,2,1,3,2], y = [5,3,4,6,2]
+
+**Output:** 14
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+* Choose `i = 0` (`x[i] = 1`, `y[i] = 5`), `j = 1` (`x[j] = 2`, `y[j] = 3`), `k = 3` (`x[k] = 3`, `y[k] = 6`).
+* All three values chosen from `x` are distinct. `5 + 3 + 6 = 14` is the maximum we can obtain. Hence, the output is 14.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** x = [1,2,1,2], y = [4,5,6,7]
+
+**Output:** \-1
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+* There are only two distinct values in `x`. Hence, the output is -1.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `n == x.length == y.length`
+* 3 <= n <= 105
+* 1 <= x[i], y[i] <= 106
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3573_best_time_to_buy_and_sell_stock_v/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3573_best_time_to_buy_and_sell_stock_v/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..a6292a37
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3573_best_time_to_buy_and_sell_stock_v/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3573_best_time_to_buy_and_sell_stock_v
+
+// #Medium #Array #Dynamic_Programming #2025_06_10_Time_27_ms_(100.00%)_Space_48.69_MB_(80.00%)
+
+import kotlin.math.max
+
+class Solution {
+ fun maximumProfit(prices: IntArray, k: Int): Long {
+ val n = prices.size
+ var prev = LongArray(n)
+ var curr = LongArray(n)
+ for (t in 1..k) {
+ var bestLong = -prices[0].toLong()
+ var bestShort = prices[0].toLong()
+ curr[0] = 0
+ for (i in 1..ith day, and an integer `k`.
+
+You are allowed to make at most `k` transactions, where each transaction can be either of the following:
+
+* **Normal transaction**: Buy on day `i`, then sell on a later day `j` where `i < j`. You profit `prices[j] - prices[i]`.
+
+* **Short selling transaction**: Sell on day `i`, then buy back on a later day `j` where `i < j`. You profit `prices[i] - prices[j]`.
+
+
+**Note** that you must complete each transaction before starting another. Additionally, you can't buy or sell on the same day you are selling or buying back as part of a previous transaction.
+
+Return the **maximum** total profit you can earn by making **at most** `k` transactions.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** prices = [1,7,9,8,2], k = 2
+
+**Output:** 14
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+We can make $14 of profit through 2 transactions:
+
+* A normal transaction: buy the stock on day 0 for $1 then sell it on day 2 for $9.
+* A short selling transaction: sell the stock on day 3 for $8 then buy back on day 4 for $2.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** prices = [12,16,19,19,8,1,19,13,9], k = 3
+
+**Output:** 36
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+We can make $36 of profit through 3 transactions:
+
+* A normal transaction: buy the stock on day 0 for $12 then sell it on day 2 for $19.
+* A short selling transaction: sell the stock on day 3 for $19 then buy back on day 4 for $8.
+* A normal transaction: buy the stock on day 5 for $1 then sell it on day 6 for $19.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 2 <= prices.length <= 103
+* 1 <= prices[i] <= 109
+* `1 <= k <= prices.length / 2`
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3574_maximize_subarray_gcd_score/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3574_maximize_subarray_gcd_score/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..31899e62
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3574_maximize_subarray_gcd_score/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3574_maximize_subarray_gcd_score
+
+// #Hard #Array #Math #Enumeration #Number_Theory
+// #2025_06_10_Time_19_ms_(100.00%)_Space_50.12_MB_(100.00%)
+
+import kotlin.math.max
+
+class Solution {
+ fun maxGCDScore(nums: IntArray, k: Int): Long {
+ var mx = 0
+ for (x in nums) {
+ mx = max(mx, x)
+ }
+ val width = 32 - Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(mx)
+ val lowBitPos: Array> = Array>(width) { _ -> ArrayList() }
+ val intervals = Array(width + 1) { IntArray(3) }
+ var size = 0
+ var ans: Long = 0
+ for (i in nums.indices) {
+ val x = nums[i]
+ val tz = Integer.numberOfTrailingZeros(x)
+ lowBitPos[tz].add(i)
+ for (j in 0.. k) max(l, pos[pos.size - k - 1]) else l
+ if (minL < r) {
+ ans = max(ans, g.toLong() * 2 * (i - minL))
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return ans
+ }
+
+ private fun gcd(a: Int, b: Int): Int {
+ var a = a
+ var b = b
+ while (a != 0) {
+ val tmp = a
+ a = b % a
+ b = tmp
+ }
+ return b
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3574_maximize_subarray_gcd_score/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3574_maximize_subarray_gcd_score/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..09b9789e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3574_maximize_subarray_gcd_score/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
+3574\. Maximize Subarray GCD Score
+
+Hard
+
+You are given an array of positive integers `nums` and an integer `k`.
+
+You may perform at most `k` operations. In each operation, you can choose one element in the array and **double** its value. Each element can be doubled **at most** once.
+
+The **score** of a contiguous **subarray** is defined as the **product** of its length and the _greatest common divisor (GCD)_ of all its elements.
+
+Your task is to return the **maximum** **score** that can be achieved by selecting a contiguous subarray from the modified array.
+
+**Note:**
+
+* The **greatest common divisor (GCD)** of an array is the largest integer that evenly divides all the array elements.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [2,4], k = 1
+
+**Output:** 8
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+* Double `nums[0]` to 4 using one operation. The modified array becomes `[4, 4]`.
+* The GCD of the subarray `[4, 4]` is 4, and the length is 2.
+* Thus, the maximum possible score is `2 × 4 = 8`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [3,5,7], k = 2
+
+**Output:** 14
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+* Double `nums[2]` to 14 using one operation. The modified array becomes `[3, 5, 14]`.
+* The GCD of the subarray `[14]` is 14, and the length is 1.
+* Thus, the maximum possible score is `1 × 14 = 14`.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [5,5,5], k = 1
+
+**Output:** 15
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+* The subarray `[5, 5, 5]` has a GCD of 5, and its length is 3.
+* Since doubling any element doesn't improve the score, the maximum score is `3 × 5 = 15`.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= n == nums.length <= 1500`
+* 1 <= nums[i] <= 109
+* `1 <= k <= n`
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3575_maximum_good_subtree_score/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3575_maximum_good_subtree_score/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..00b7b92a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3575_maximum_good_subtree_score/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3575_maximum_good_subtree_score
+
+// #Hard #Array #Dynamic_Programming #Depth_First_Search #Tree #Bit_Manipulation #Bitmask
+// #2025_06_10_Time_71_ms_(100.00%)_Space_78.07_MB_(0.00%)
+
+import kotlin.math.max
+
+class Solution {
+ private val digits = 10
+ private val full = 1 shl digits
+ private val neg = Long.Companion.MIN_VALUE / 4
+ private val mod = 1e9.toLong() + 7
+ private lateinit var tree: Array>
+ private lateinit var `val`: IntArray
+ private lateinit var mask: IntArray
+ private lateinit var isOk: BooleanArray
+ private var res: Long = 0
+
+ fun goodSubtreeSum(vals: IntArray, par: IntArray): Int {
+ val n = vals.size
+ `val` = vals
+ mask = IntArray(n)
+ isOk = BooleanArray(n)
+ for (i in 0.. 0) {
+ val d = v % 10
+ if (((m shr d) and 1) == 1) {
+ valid = false
+ break
+ }
+ m = m or (1 shl d)
+ v /= 10
+ }
+ mask[i] = m
+ isOk[i] = valid
+ }
+ tree = Array(n) { initialCapacity: Int -> ArrayList(initialCapacity) }
+ val root = 0
+ for (i in 1.. 0) {
+ if (child[m2] < 0) {
+ m2 = (m2 - 1) and remain
+ continue
+ }
+ val newM = m1 or m2
+ newDp[newM] = max(newDp[newM], dp[m1] + child[m2])
+ m2 = (m2 - 1) and remain
+ }
+ }
+ dp = newDp
+ }
+ var best: Long = 0
+ for (v in dp) {
+ best = max(best, v)
+ }
+ res = (res + best) % mod
+ return dp
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3575_maximum_good_subtree_score/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3575_maximum_good_subtree_score/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..bb1a07b9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3575_maximum_good_subtree_score/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
+3575\. Maximum Good Subtree Score
+
+Hard
+
+You are given an undirected tree rooted at node 0 with `n` nodes numbered from 0 to `n - 1`. Each node `i` has an integer value `vals[i]`, and its parent is given by `par[i]`.
+
+A **subset** of nodes within the **subtree** of a node is called **good** if every digit from 0 to 9 appears **at most** once in the decimal representation of the values of the selected nodes.
+
+The **score** of a good subset is the sum of the values of its nodes.
+
+Define an array `maxScore` of length `n`, where `maxScore[u]` represents the **maximum** possible sum of values of a good subset of nodes that belong to the subtree rooted at node `u`, including `u` itself and all its descendants.
+
+Return the sum of all values in `maxScore`.
+
+Since the answer may be large, return it **modulo** 109 + 7.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** vals = [2,3], par = [-1,0]
+
+**Output:** 8
+
+**Explanation:**
+
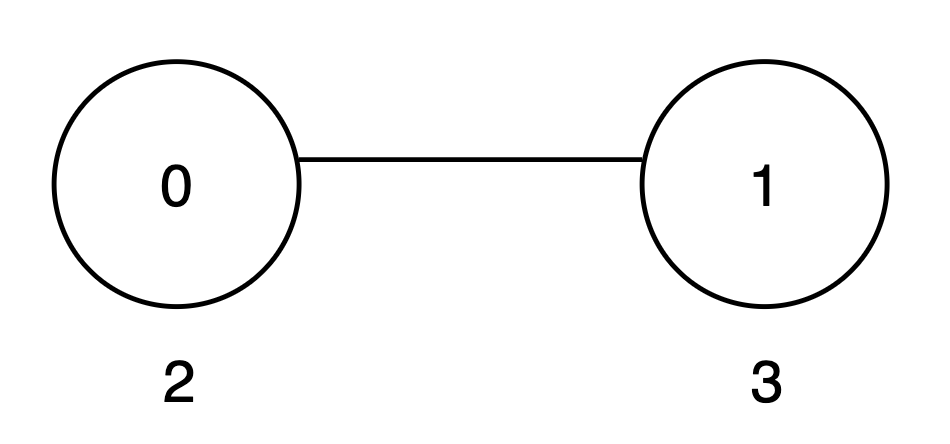
+
+
+* The subtree rooted at node 0 includes nodes `{0, 1}`. The subset `{2, 3}` is good as the digits 2 and 3 appear only once. The score of this subset is `2 + 3 = 5`.
+* The subtree rooted at node 1 includes only node `{1}`. The subset `{3}` is good. The score of this subset is 3.
+* The `maxScore` array is `[5, 3]`, and the sum of all values in `maxScore` is `5 + 3 = 8`. Thus, the answer is 8.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** vals = [1,5,2], par = [-1,0,0]
+
+**Output:** 15
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+**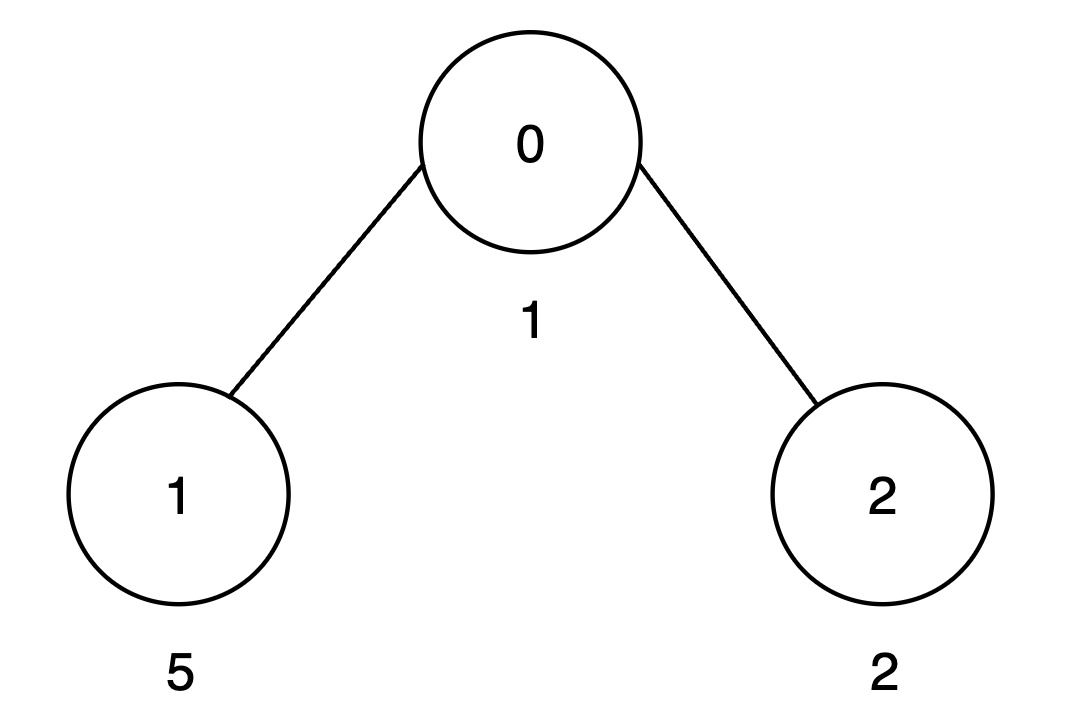**
+
+* The subtree rooted at node 0 includes nodes `{0, 1, 2}`. The subset `{1, 5, 2}` is good as the digits 1, 5 and 2 appear only once. The score of this subset is `1 + 5 + 2 = 8`.
+* The subtree rooted at node 1 includes only node `{1}`. The subset `{5}` is good. The score of this subset is 5.
+* The subtree rooted at node 2 includes only node `{2}`. The subset `{2}` is good. The score of this subset is 2.
+* The `maxScore` array is `[8, 5, 2]`, and the sum of all values in `maxScore` is `8 + 5 + 2 = 15`. Thus, the answer is 15.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** vals = [34,1,2], par = [-1,0,1]
+
+**Output:** 42
+
+**Explanation:**
+
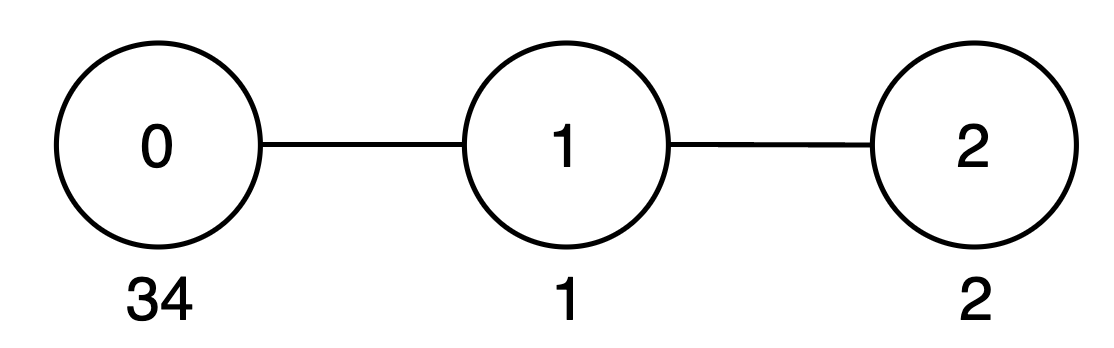
+
+
+* The subtree rooted at node 0 includes nodes `{0, 1, 2}`. The subset `{34, 1, 2}` is good as the digits 3, 4, 1 and 2 appear only once. The score of this subset is `34 + 1 + 2 = 37`.
+* The subtree rooted at node 1 includes node `{1, 2}`. The subset `{1, 2}` is good as the digits 1 and 2 appear only once. The score of this subset is `1 + 2 = 3`.
+* The subtree rooted at node 2 includes only node `{2}`. The subset `{2}` is good. The score of this subset is 2.
+* The `maxScore` array is `[37, 3, 2]`, and the sum of all values in `maxScore` is `37 + 3 + 2 = 42`. Thus, the answer is 42.
+
+**Example 4:**
+
+**Input:** vals = [3,22,5], par = [-1,0,1]
+
+**Output:** 18
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+* The subtree rooted at node 0 includes nodes `{0, 1, 2}`. The subset `{3, 22, 5}` is not good, as digit 2 appears twice. Therefore, the subset `{3, 5}` is valid. The score of this subset is `3 + 5 = 8`.
+* The subtree rooted at node 1 includes nodes `{1, 2}`. The subset `{22, 5}` is not good, as digit 2 appears twice. Therefore, the subset `{5}` is valid. The score of this subset is 5.
+* The subtree rooted at node 2 includes `{2}`. The subset `{5}` is good. The score of this subset is 5.
+* The `maxScore` array is `[8, 5, 5]`, and the sum of all values in `maxScore` is `8 + 5 + 5 = 18`. Thus, the answer is 18.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= n == vals.length <= 500`
+* 1 <= vals[i] <= 109
+* `par.length == n`
+* `par[0] == -1`
+* `0 <= par[i] < n` for `i` in `[1, n - 1]`
+* The input is generated such that the parent array `par` represents a valid tree.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3576_transform_array_to_all_equal_elements/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3576_transform_array_to_all_equal_elements/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..cdf515c4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3576_transform_array_to_all_equal_elements/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3576_transform_array_to_all_equal_elements
+
+// #Medium #Array #Greedy #2025_06_10_Time_11_ms_(92.31%)_Space_84.38_MB_(15.38%)
+
+class Solution {
+ fun canMakeEqual(nums: IntArray, k: Int): Boolean {
+ val n = nums.size
+ if (n == 1) {
+ return true
+ }
+ var prod = 1
+ for (x in nums) {
+ prod *= x
+ }
+ val targets: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ for (target in intArrayOf(1, -1)) {
+ val tPowN = (if (n % 2 == 0) 1 else target)
+ if (tPowN == prod) {
+ targets.add(target)
+ }
+ }
+ if (targets.isEmpty()) {
+ return false
+ }
+ for (target in targets) {
+ var ops = 0
+ val a = nums.clone()
+ var i = 0
+ while (i < n - 1 && ops <= k) {
+ if (a[i] != target) {
+ a[i] = -a[i]
+ a[i + 1] = -a[i + 1]
+ ops++
+ }
+ i++
+ }
+ if (ops <= k && a[n - 1] == target) {
+ return true
+ }
+ }
+ return false
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3576_transform_array_to_all_equal_elements/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3576_transform_array_to_all_equal_elements/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..61c7d394
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3576_transform_array_to_all_equal_elements/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
+3576\. Transform Array to All Equal Elements
+
+Medium
+
+You are given an integer array `nums` of size `n` containing only `1` and `-1`, and an integer `k`.
+
+You can perform the following operation at most `k` times:
+
+* Choose an index `i` (`0 <= i < n - 1`), and **multiply** both `nums[i]` and `nums[i + 1]` by `-1`.
+
+
+**Note** that you can choose the same index `i` more than once in **different** operations.
+
+Return `true` if it is possible to make all elements of the array **equal** after at most `k` operations, and `false` otherwise.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,-1,1,-1,1], k = 3
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+We can make all elements in the array equal in 2 operations as follows:
+
+* Choose index `i = 1`, and multiply both `nums[1]` and `nums[2]` by -1. Now `nums = [1,1,-1,-1,1]`.
+* Choose index `i = 2`, and multiply both `nums[2]` and `nums[3]` by -1. Now `nums = [1,1,1,1,1]`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [-1,-1,-1,1,1,1], k = 5
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+It is not possible to make all array elements equal in at most 5 operations.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= n == nums.length <= 105
+* `nums[i]` is either -1 or 1.
+* `1 <= k <= n`
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3577_count_the_number_of_computer_unlocking_permutations/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3577_count_the_number_of_computer_unlocking_permutations/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d0763578
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3577_count_the_number_of_computer_unlocking_permutations/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3577_count_the_number_of_computer_unlocking_permutations
+
+// #Medium #Array #Math #Combinatorics #Brainteaser
+// #2025_06_10_Time_2_ms_(100.00%)_Space_70.49_MB_(30.00%)
+
+class Solution {
+ fun countPermutations(complexity: IntArray): Int {
+ val n = complexity.size
+ for (i in 1..9 + 7.
+
+**Note** that the password for the computer **with label** 0 is decrypted, and _not_ the computer with the first position in the permutation.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** complexity = [1,2,3]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The valid permutations are:
+
+* [0, 1, 2]
+ * Unlock computer 0 first with root password.
+ * Unlock computer 1 with password of computer 0 since `complexity[0] < complexity[1]`.
+ * Unlock computer 2 with password of computer 1 since `complexity[1] < complexity[2]`.
+* [0, 2, 1]
+ * Unlock computer 0 first with root password.
+ * Unlock computer 2 with password of computer 0 since `complexity[0] < complexity[2]`.
+ * Unlock computer 1 with password of computer 0 since `complexity[0] < complexity[1]`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** complexity = [3,3,3,4,4,4]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+There are no possible permutations which can unlock all computers.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 2 <= complexity.length <= 105
+* 1 <= complexity[i] <= 109
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3578_count_partitions_with_max_min_difference_at_most_k/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3578_count_partitions_with_max_min_difference_at_most_k/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d370770a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3578_count_partitions_with_max_min_difference_at_most_k/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3578_count_partitions_with_max_min_difference_at_most_k
+
+// #Medium #Array #Dynamic_Programming #Prefix_Sum #Sliding_Window #Queue #Monotonic_Queue
+// #2025_06_10_Time_33_ms_(100.00%)_Space_74.03_MB_(66.67%)
+
+class Solution {
+ fun countPartitions(nums: IntArray, k: Int): Int {
+ val n = nums.size
+ val dp = IntArray(n + 1)
+ dp[0] = 1
+ val prefix = IntArray(n + 1)
+ prefix[0] = 1
+ val maxDeque = IntArray(n)
+ var maxFront = 0
+ var maxBack = 0
+ val minDeque = IntArray(n)
+ var minFront = 0
+ var minBack = 0
+ var start = 0
+ for (end in 0.. maxFront && nums[maxDeque[maxBack - 1]] <= nums[end]) {
+ maxBack--
+ }
+ maxDeque[maxBack++] = end
+ while (minBack > minFront && nums[minDeque[minBack - 1]] >= nums[end]) {
+ minBack--
+ }
+ minDeque[minBack++] = end
+ while (nums[maxDeque[maxFront]] - nums[minDeque[minFront]] > k) {
+ if (maxDeque[maxFront] == start) {
+ maxFront++
+ }
+ if (minDeque[minFront] == start) {
+ minFront++
+ }
+ start++
+ }
+ var sum = prefix[end] - (if (start > 0) prefix[start - 1] else 0)
+ if (sum < 0) {
+ sum += MOD
+ }
+ dp[end + 1] = sum % MOD
+ prefix[end + 1] = (prefix[end] + dp[end + 1]) % MOD
+ }
+ return dp[n]
+ }
+
+ companion object {
+ private const val MOD = 1000000007
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3578_count_partitions_with_max_min_difference_at_most_k/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3578_count_partitions_with_max_min_difference_at_most_k/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..7bb809d5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3578_count_partitions_with_max_min_difference_at_most_k/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
+3578\. Count Partitions With Max-Min Difference at Most K
+
+Medium
+
+You are given an integer array `nums` and an integer `k`. Your task is to partition `nums` into one or more **non-empty** contiguous segments such that in each segment, the difference between its **maximum** and **minimum** elements is **at most** `k`.
+
+Return the total number of ways to partition `nums` under this condition.
+
+Since the answer may be too large, return it **modulo** 109 + 7.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [9,4,1,3,7], k = 4
+
+**Output:** 6
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+There are 6 valid partitions where the difference between the maximum and minimum elements in each segment is at most `k = 4`:
+
+* `[[9], [4], [1], [3], [7]]`
+* `[[9], [4], [1], [3, 7]]`
+* `[[9], [4], [1, 3], [7]]`
+* `[[9], [4, 1], [3], [7]]`
+* `[[9], [4, 1], [3, 7]]`
+* `[[9], [4, 1, 3], [7]]`
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [3,3,4], k = 0
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+There are 2 valid partitions that satisfy the given conditions:
+
+* `[[3], [3], [4]]`
+* `[[3, 3], [4]]`
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 2 <= nums.length <= 5 * 104
+* 1 <= nums[i] <= 109
+* 0 <= k <= 109
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3579_minimum_steps_to_convert_string_with_operations/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3579_minimum_steps_to_convert_string_with_operations/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0dd56d4e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3579_minimum_steps_to_convert_string_with_operations/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3579_minimum_steps_to_convert_string_with_operations
+
+// #Hard #String #Dynamic_Programming #Greedy
+// #2025_06_10_Time_107_ms_(100.00%)_Space_48.36_MB_(100.00%)
+
+import kotlin.math.min
+
+class Solution {
+ fun minOperations(word1: String, word2: String): Int {
+ val dp = IntArray(word1.length)
+ val count: Array = Array(26) { IntArray(26) }
+ for (i in 0.. 0) {
+ ints[word1[k1].code - 'a'.code]--
+ } else if (word1[k1] != word2[k2]) {
+ count[word1[k1].code - 'a'.code][word2[k2].code - 'a'.code]++
+ c1++
+ }
+ k1++
+ k2++
+ }
+ }
+ run {
+ var k1 = j
+ var k2 = j
+ while (k1 <= i && k2 <= i) {
+ count[word1[k1].code - 'a'.code][word2[k2].code - 'a'.code] = 0
+ k1++
+ k2++
+ }
+ }
+ dp[i] = min(dp[i], if (j - 1 < 0) c1 else dp[j - 1] + c1)
+ run {
+ var k1 = j
+ var k2 = i
+ while (k1 <= i && k2 >= j) {
+ val ints = count[word2[k2].code - 'a'.code]
+ if (ints[word1[k1].code - 'a'.code] > 0) {
+ ints[word1[k1].code - 'a'.code]--
+ } else if (word1[k1].code - 'a'.code != word2[k2].code - 'a'.code) {
+ count[word1[k1].code - 'a'.code][word2[k2].code - 'a'.code]++
+ c2++
+ }
+ k1++
+ k2--
+ }
+ }
+ var k1 = j
+ var k2 = i
+ while (k1 <= i && k2 >= j) {
+ count[word1[k1].code - 'a'.code][word2[k2].code - 'a'.code] = 0
+ k1++
+ k2--
+ }
+ dp[i] = min(dp[i], if (j - 1 < 0) c2 + 1 else dp[j - 1] + c2 + 1)
+ }
+ }
+ return dp[word1.length - 1]
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3579_minimum_steps_to_convert_string_with_operations/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3579_minimum_steps_to_convert_string_with_operations/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..daca3491
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3579_minimum_steps_to_convert_string_with_operations/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
+3579\. Minimum Steps to Convert String with Operations
+
+Hard
+
+You are given two strings, `word1` and `word2`, of equal length. You need to transform `word1` into `word2`.
+
+For this, divide `word1` into one or more **contiguous **substring****. For each substring `substr` you can perform the following operations:
+
+1. **Replace:** Replace the character at any one index of `substr` with another lowercase English letter.
+
+2. **Swap:** Swap any two characters in `substr`.
+
+3. **Reverse Substring:** Reverse `substr`.
+
+
+Each of these counts as **one** operation and each character of each substring can be used in each type of operation at most once (i.e. no single index may be involved in more than one replace, one swap, or one reverse).
+
+Return the **minimum number of operations** required to transform `word1` into `word2`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** word1 = "abcdf", word2 = "dacbe"
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Divide `word1` into `"ab"`, `"c"`, and `"df"`. The operations are:
+
+* For the substring `"ab"`,
+ * Perform operation of type 3 on `"ab" -> "ba"`.
+ * Perform operation of type 1 on `"ba" -> "da"`.
+* For the substring `"c"` do no operations.
+* For the substring `"df"`,
+ * Perform operation of type 1 on `"df" -> "bf"`.
+ * Perform operation of type 1 on `"bf" -> "be"`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** word1 = "abceded", word2 = "baecfef"
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Divide `word1` into `"ab"`, `"ce"`, and `"ded"`. The operations are:
+
+* For the substring `"ab"`,
+ * Perform operation of type 2 on `"ab" -> "ba"`.
+* For the substring `"ce"`,
+ * Perform operation of type 2 on `"ce" -> "ec"`.
+* For the substring `"ded"`,
+ * Perform operation of type 1 on `"ded" -> "fed"`.
+ * Perform operation of type 1 on `"fed" -> "fef"`.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** word1 = "abcdef", word2 = "fedabc"
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Divide `word1` into `"abcdef"`. The operations are:
+
+* For the substring `"abcdef"`,
+ * Perform operation of type 3 on `"abcdef" -> "fedcba"`.
+ * Perform operation of type 2 on `"fedcba" -> "fedabc"`.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= word1.length == word2.length <= 100`
+* `word1` and `word2` consist only of lowercase English letters.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3572_maximize_ysum_by_picking_a_triplet_of_distinct_xvalues/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3572_maximize_ysum_by_picking_a_triplet_of_distinct_xvalues/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..d74d0ad5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3572_maximize_ysum_by_picking_a_triplet_of_distinct_xvalues/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3572_maximize_ysum_by_picking_a_triplet_of_distinct_xvalues
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun maxSumDistinctTriplet() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution()
+ .maxSumDistinctTriplet(
+ intArrayOf(1, 2, 1, 3, 2),
+ intArrayOf(5, 3, 4, 6, 2),
+ ),
+ equalTo(14),
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun maxSumDistinctTriplet2() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution()
+ .maxSumDistinctTriplet(intArrayOf(1, 2, 1, 2), intArrayOf(4, 5, 6, 7)),
+ equalTo(-1),
+ )
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3573_best_time_to_buy_and_sell_stock_v/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3573_best_time_to_buy_and_sell_stock_v/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..53de3e13
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3573_best_time_to_buy_and_sell_stock_v/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3573_best_time_to_buy_and_sell_stock_v
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun maximumProfit() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().maximumProfit(intArrayOf(1, 7, 9, 8, 2), 2),
+ equalTo(14L),
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun maximumProfit2() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().maximumProfit(intArrayOf(12, 16, 19, 19, 8, 1, 19, 13, 9), 3),
+ equalTo(36L),
+ )
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3574_maximize_subarray_gcd_score/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3574_maximize_subarray_gcd_score/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c0b6f9d7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3574_maximize_subarray_gcd_score/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3574_maximize_subarray_gcd_score
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun maxGCDScore() {
+ assertThat(Solution().maxGCDScore(intArrayOf(2, 4), 1), equalTo(8L))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun maxGCDScore2() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().maxGCDScore(intArrayOf(3, 5, 7), 2),
+ equalTo(14L),
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun maxGCDScore3() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().maxGCDScore(intArrayOf(5, 5, 5), 1),
+ equalTo(15L),
+ )
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3575_maximum_good_subtree_score/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3575_maximum_good_subtree_score/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c88256cb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3575_maximum_good_subtree_score/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3575_maximum_good_subtree_score
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun goodSubtreeSum() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().goodSubtreeSum(intArrayOf(2, 3), intArrayOf(-1, 0)),
+ equalTo(8),
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun goodSubtreeSum2() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().goodSubtreeSum(intArrayOf(1, 5, 2), intArrayOf(-1, 0, 0)),
+ equalTo(15),
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun goodSubtreeSum3() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().goodSubtreeSum(intArrayOf(34, 1, 2), intArrayOf(-1, 0, 1)),
+ equalTo(42),
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun goodSubtreeSum4() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().goodSubtreeSum(intArrayOf(3, 22, 5), intArrayOf(-1, 0, 1)),
+ equalTo(18),
+ )
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3576_transform_array_to_all_equal_elements/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3576_transform_array_to_all_equal_elements/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c04dcb30
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3576_transform_array_to_all_equal_elements/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3576_transform_array_to_all_equal_elements
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun canMakeEqual() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().canMakeEqual(intArrayOf(1, -1, 1, -1, 1), 3),
+ equalTo(true),
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun canMakeEqual2() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().canMakeEqual(intArrayOf(-1, -1, -1, 1, 1, 1), 5),
+ equalTo(false),
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun canMakeEqual3() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().canMakeEqual(intArrayOf(1), 3),
+ equalTo(true),
+ )
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3577_count_the_number_of_computer_unlocking_permutations/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3577_count_the_number_of_computer_unlocking_permutations/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..daa39a95
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3577_count_the_number_of_computer_unlocking_permutations/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3577_count_the_number_of_computer_unlocking_permutations
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun countPermutations() {
+ assertThat(Solution().countPermutations(intArrayOf(1, 2, 3)), equalTo(2))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun countPermutations2() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().countPermutations(intArrayOf(3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4)),
+ equalTo(0),
+ )
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3578_count_partitions_with_max_min_difference_at_most_k/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3578_count_partitions_with_max_min_difference_at_most_k/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..b421cc8e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3578_count_partitions_with_max_min_difference_at_most_k/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3578_count_partitions_with_max_min_difference_at_most_k
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun countPartitions() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().countPartitions(intArrayOf(9, 4, 1, 3, 7), 4),
+ equalTo(6),
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun countPartitions2() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().countPartitions(intArrayOf(3, 3, 4), 0),
+ equalTo(2),
+ )
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3579_minimum_steps_to_convert_string_with_operations/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3579_minimum_steps_to_convert_string_with_operations/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..df1eae19
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3579_minimum_steps_to_convert_string_with_operations/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3579_minimum_steps_to_convert_string_with_operations
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun minOperations() {
+ assertThat(Solution().minOperations("abcdf", "dacbe"), equalTo(4))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun minOperations2() {
+ assertThat(Solution().minOperations("abceded", "baecfef"), equalTo(4))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun minOperations3() {
+ assertThat(Solution().minOperations("abcdef", "fedabc"), equalTo(2))
+ }
+}