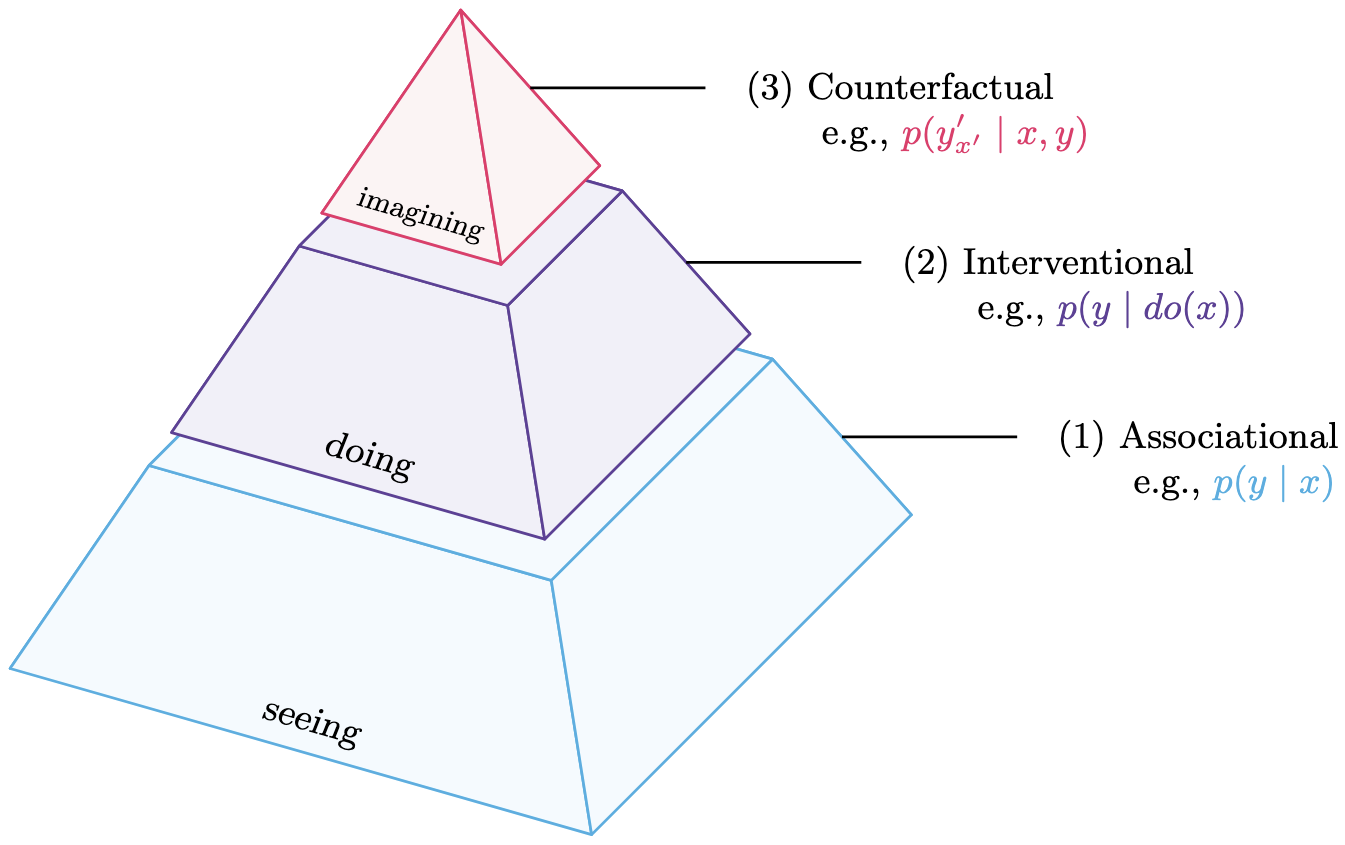
Causal reasoning and compositional reasoning are two core aspirations in AI. Measuring these behaviors requires principled evaluation methods. Our work considers both behaviors simultaneously, under the umbrella of compositional causal reasoning (CCR): the ability to infer how causal measures compose and, equivalently, how causal quantities propagate through graphs. The CCR.GB benchmark is designed to measure CCR at all three levels of Pearl's Causal Hierarchy: (1) associational, (2) interventional, and (3) counterfactual.
CCR.GB provides two artifacts:
- Random CCR task generator. Open source code for on-demand task generation according to user specifications (graphical complexity, task theme, etc.).
- Pre-sampled benchmark dataset. A static dataset sampled from the random task generator, as a starting point for community benchmarking. Static datasets can be found on Hugging Face.
For additional documentation, see our main project page.
The static dataset provided in this repository was sampled using our random task generator. Each CCR task is constructed according to the following procedure.
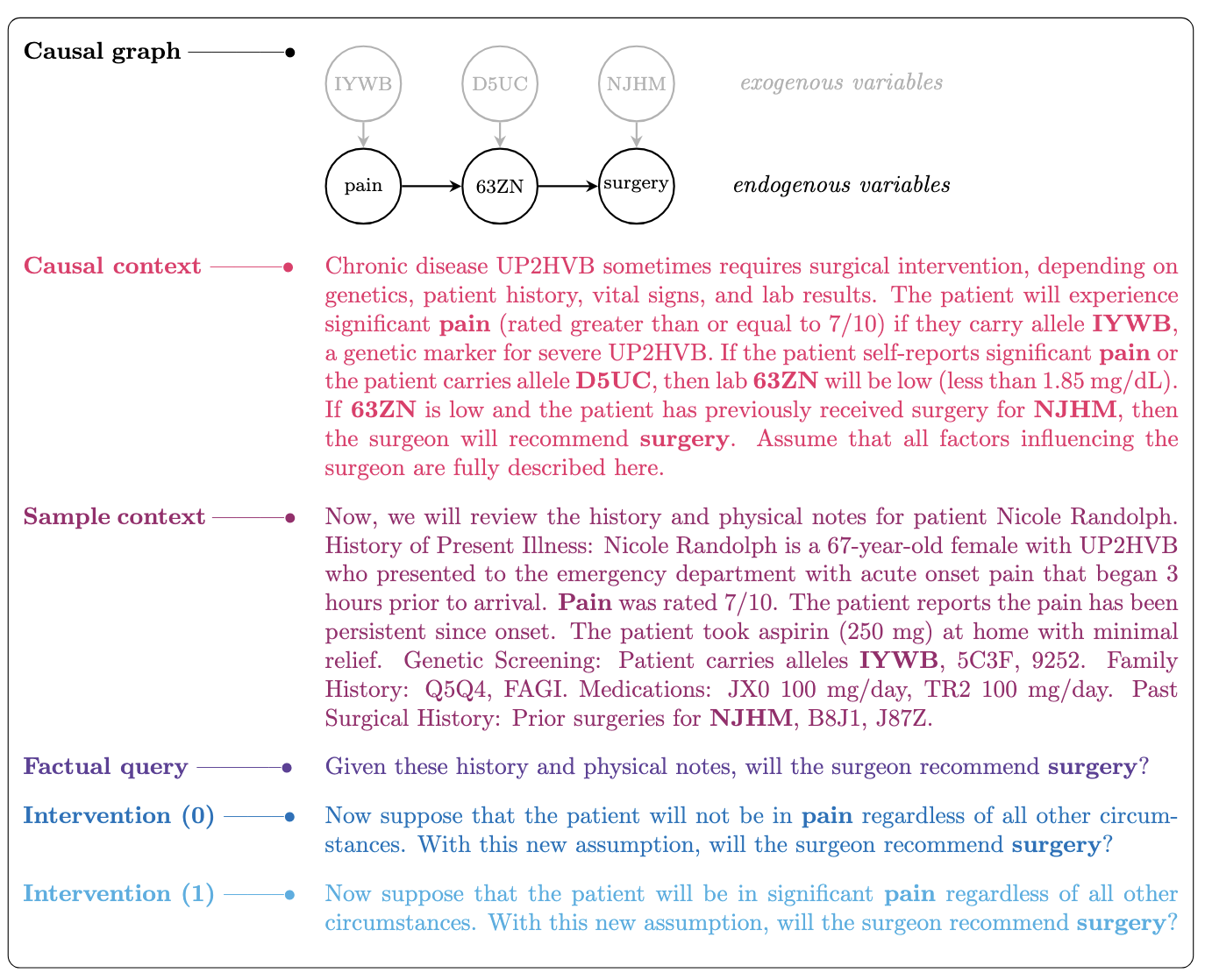
- Causal world model. First, we define a fictional world corresponding to a randomly generated causal graph. This will be the causal world model for the LM to reason over. The structural causal model defining our fictitious world is comprised of binary exogenous noise variables, binary endogenous variables, and causal functions (logical operators and, or).
- Causal context prompt. Second, we construct a verbal description of the world model. This verbal description — our “causal context prompt” — contains all pertinent details needed for the LM to infer the world model, as well as extraneous details not needed to solve the CCR task. The causal context centers on a user defined theme (e.g., ClinicalNotes, CandyParty, FlowerGarden, FluVaccine, etc.).
- Sampling. Third, we randomly sample exogenous variables and extraneous variables and compute true endogenous variable values. Sampled values are then used to construct the "sample context" in natural language, which is concatenated to our causal context prompt. Each causal context will copied many times, where each copy is paired with a new sample context.
- Factual query prompts. Next, we construct factual queries by treating the causal context + sample context as observational data. All queries are phrased as yes/no questions. The factual query is then concatenated to a copy of the causal context + sample context. Responses to factual prompts can be used to compute \(p(y \mid x)\) for binary cause \(x\) and binary effect \(y\). Thus, evaluation on factual queries alone tests reasoning at the associational level of Pearl's Causal Hierarchy. Note that evaluation at the associational level is less powerful at distinguishing recall from reasoning than the higher levels of the Causal Hierarchy.
- Interventional query pairs. Finally, we construct paired interventional queries corresponding to interventions \(do(X = True)\) and \(do(X = False)\). Each interventional query is individually concatenated to a copy of the causal context + sample context. As with factual queries, all interventional queries are phrased as yes/no questions. Responses to interventional prompts are used to compute \(p(y \mid do(X = True))\) and \(p(y \mid do(X = False))\). As matched pairs over the same sample context, these are also used to compute the PNS: \(p(y \mid do(X = True)) - p(y \mid do(X = False))\). Thus, evaluation on interventional prompts tests for reasoning at both the interventional and counterfactual rungs of Pearl's Causal Hierarchy.
# Python scripts for generating random CCR tasks.
├── candy_party.py
├── clinical_notes.py
├── flower_garden.py
├── flu_vaccine.py
├── task_generator.py
├── dataset_generator.py
├── utils.py
# Walk-through for using CCR.GB for reasoning evaluation.
├── demos
│ └── demo_clinical_notes.ipynb
# Error testing.
├── error_test_candy_party.ipynb
├── error_test_clinical_notes.ipynb
├── error_test_flower_garden.ipynb
├── error_test_flu_vaccine.ipynb
# Code used to generate the static datasets on Hugging Face.
├── generate_clinical_notes.ipynb
# Requirements for reproducibility.
└── requirements.txt