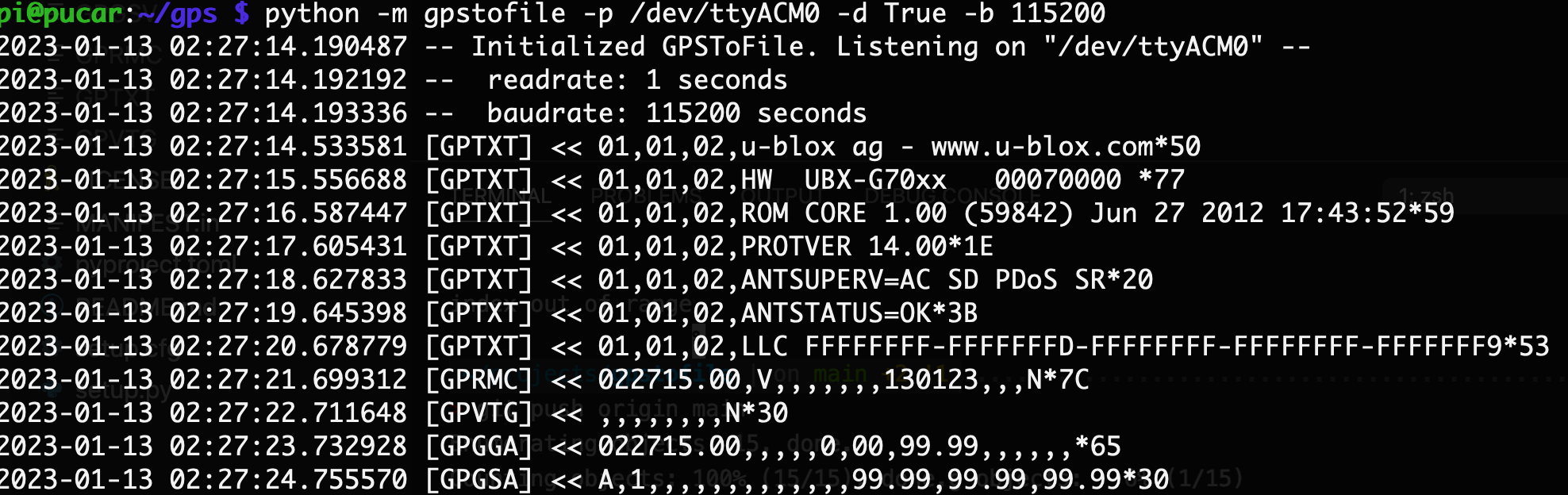
Quick and easy way to read GPS sentences to file with no gpsd required.
pip install gpstofile
Here are the available configuration options:
| Key | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| path | str | Path to serial port |
| baudrate | int | Serial port baud rate (Default: 115200) |
| readrate | int | Read interval to listen for GPS sentences on serial bus (Default: 0s) |
| debug | bool | Print verbose log statements for debugging purposes (Default: False) |
| append | bool | Append to file instead of overwriting file contents on each new message received (Default: False) |
Once you get the serial path of your GPS modem, you can get started either via command line, or by importing the module:
python -m gpstofile --port /dev/tty.usbmodem14401 --debug True
or:
from gpstofile import GPSToFile
gps = GPSToFile('/dev/tty.usbmodem14401', readrate=1, debug=True)
gps.loop()Once the loop begins running, GPS sentences will be written to files. You should see the files be created/continuously written to at readrate based on the codes in the following table:
The filename will be the NMEA sentence, for example GPGLL and the file contents will be the set of data sent after that sentence.
| NMEA Sentence | Meaning |
|---|---|
| GPGGA | Global positioning system fix data (time, position, fix type data) |
| GPGLL | Geographic position, latitude, longitude |
| GPVTG | Course and speed information relative to the ground |
| GPRMC | Time, date, position, course and speed data |
| GPGSA | GPS receiver operating mode, satellites used in the position solution, and DOP values. |
| GPGSV | The number of GPS satellites in view satellite ID numbers, elevation, azimuth and SNR values. |
| GPMSS | Signal to noise ratio, signal strength, frequency, and bit rate from a radio beacon receiver. |
| GPTRF | Transit fix data |
| GPSTN | Multiple data ID |
| GPXTE | cross track error, measured |
| GPZDA | Date and time (PPS timing message, synchronized to PPS). |
For more info, check out this resource from RF Wireless World.