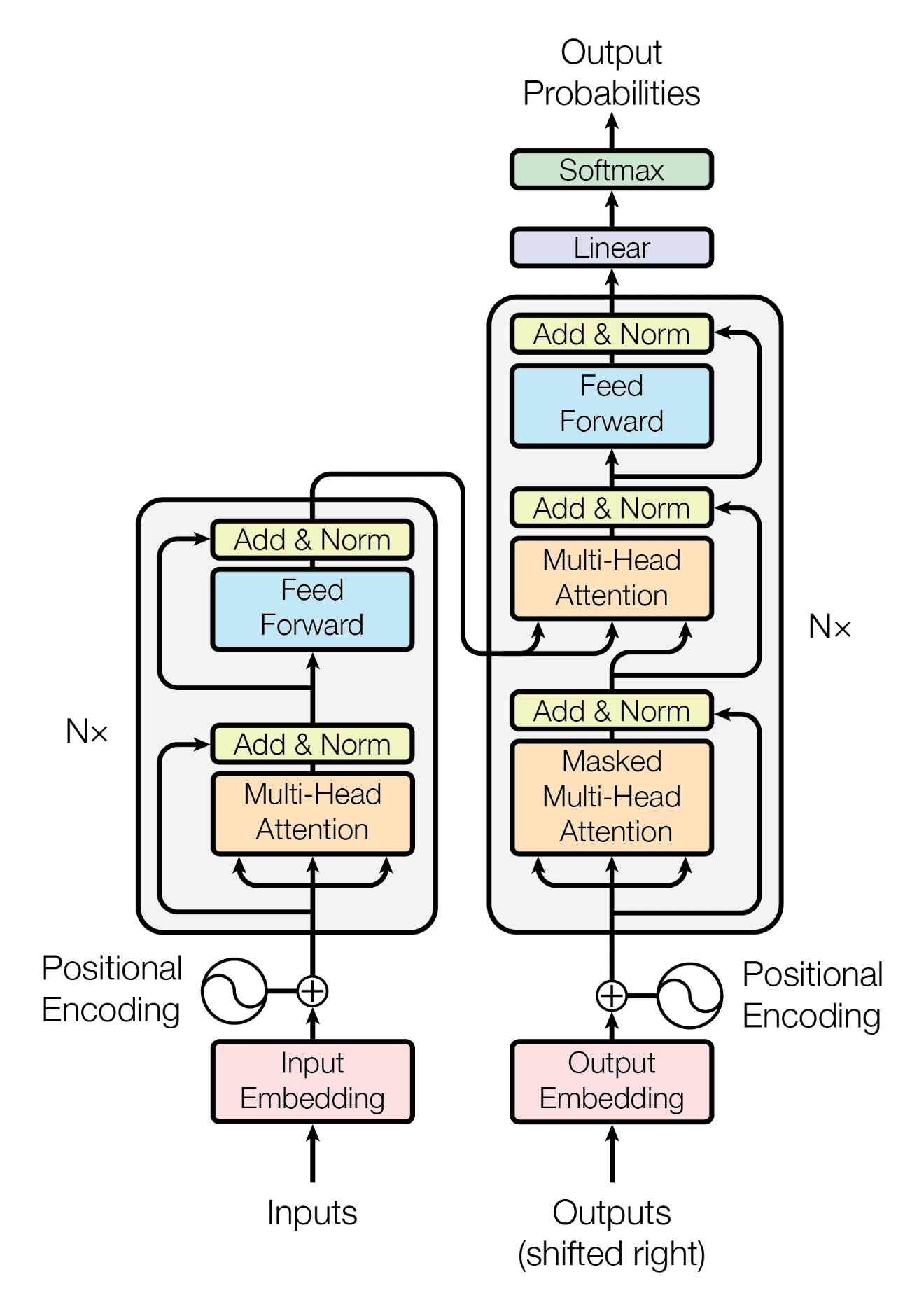
Welcome to the Machine Translation with Transformers project! This project demonstrates the implementation of a Transformer model for machine translation tasks. The Transformer model has shown great success in various natural language processing tasks, including machine translation.
To understand and use the code, follow the steps below:
-
Prepare your training data: You need to provide a CSV file containing the source language sentences and the corresponding target language sentences. The CSV file should have two columns: "source" and "target". Each row represents a sentence pair.
-
Initialize the tokenizer: The tokenizer is responsible for tokenizing the sentences and converting them into numerical representations. To initialize the tokenizer, create an instance of the Tokenizer class and load the vocabulary dictionary from a JSON file using the
load_word2idxmethod. This step ensures that the sentences are converted into a format that can be processed by the model. -
Tokenize the sentences: Use the
tokenizemethod of the tokenizer to convert the sentences into tokenized form. This step is necessary to prepare the data for training the model. Tokenization breaks down the sentences into smaller units (tokens) and assigns a unique numerical representation to each token. -
Prepare the input tensors: Pad or truncate the tokenized sentences to a fixed length using the
max_seq_lengthvariable. This ensures that all sentences have the same length, which is required for efficient training. Convert the tokenized sentences into tensors usingtorch.tensor, a data structure used by the model for computation. -
Define the Transformer model: Instantiate an instance of the Transformer class and specify the required parameters such as source and target vocabulary size, model dimensions, number of attention heads, number of layers, and dropout rate. The Transformer model consists of multiple layers of self-attention and feed-forward neural networks, enabling it to capture complex dependencies in the input sentences.
-
Train the model: Use the prepared input tensors as the input to the
forwardmethod of the Transformer model. The model will perform the forward pass, compute the output predictions, and compare them with the actual target sentences to calculate the loss. The goal of training is to minimize this loss by adjusting the model's parameters through backpropagation. Training is typically performed using optimization techniques like stochastic gradient descent (SGD) or Adam optimizer. -
Low loss performance shown: In machine translation tasks, achieving a low loss indicates that the model is effectively translating the source sentences into the target language. A low loss suggests that the model has learned to capture the patterns and relationships between the source and target sentences. Monitoring the loss during training helps assess the model's progress and determine when to stop training. The english to arabic dataset example within the notebooks shows low loss.
Feel free to explore the code and experiment with different hyperparameters, architectures, or training techniques to improve the translation quality and reduce the loss further.
Contributions are welcome! If you have any suggestions, bug reports, or feature requests, please open an issue or submit a pull request.
This project is licensed under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for more information.