-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 7
Overview
jhensl19 edited this page Jul 18, 2024
·
2 revisions
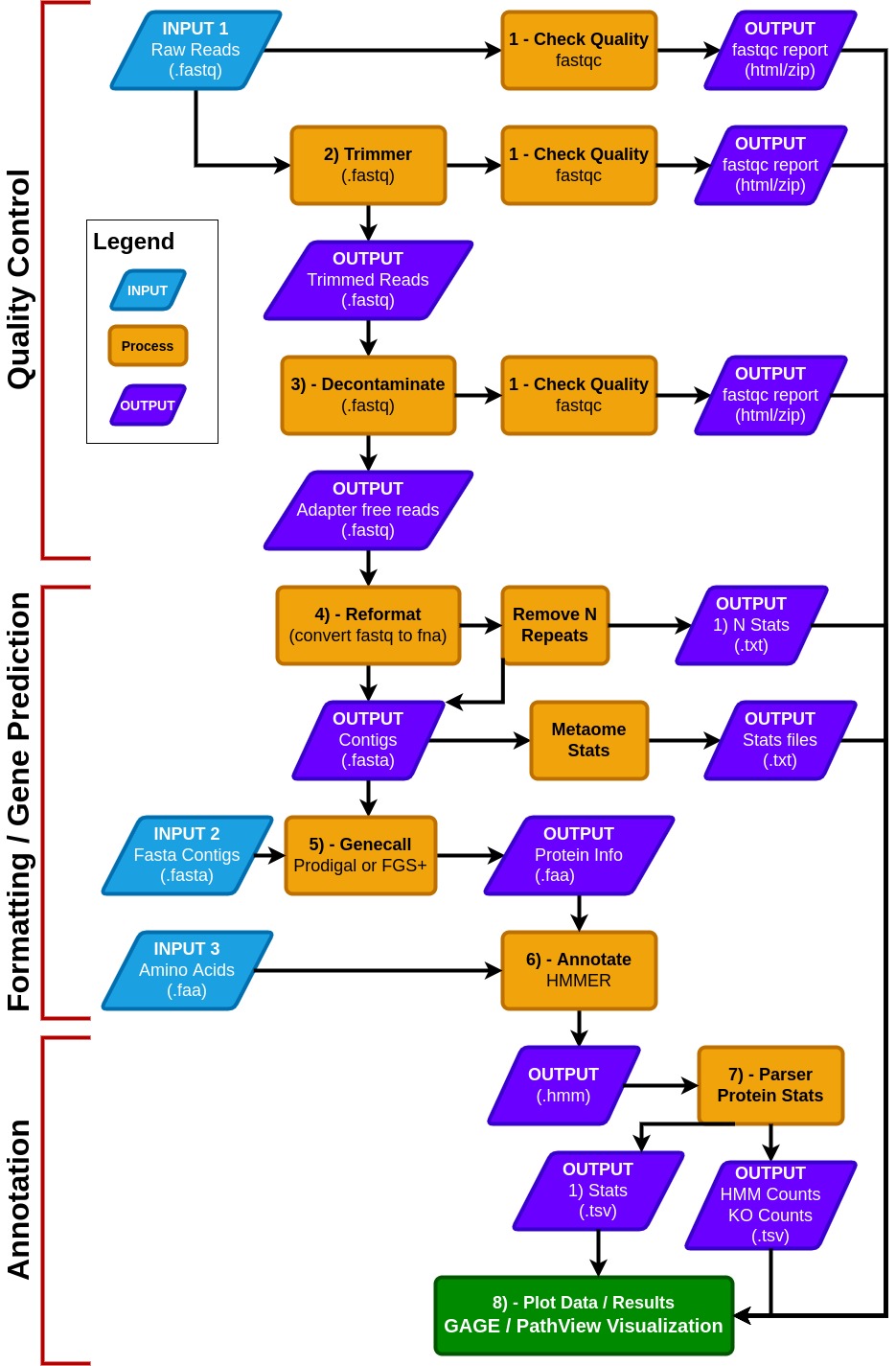
- MetaCerberus has three basic modes:
- Quality Control (QC) for raw reads
- Formatting/gene prediction
- Annotation
- MetaCerberus can use three different input files:
- Raw read data from any sequencing platform (Illumina, PacBio, or Oxford Nanopore)
- Assembled contigs, as MAGs, vMAGs, isolate genomes, or a collection of contigs
- Amino acid fasta (.faa), previously called pORFs
- We offer customization, including running all databases together, individually or specifying select databases. For example, if a user wants to run prokaryotic or eukaryotic-specific KOfams, or an individual database alone such as dbCAN, both are easily customized within MetaCerberus.
- In QC mode, raw reads are quality controlled with pre- and post-trim via FastQC. Raw reads are then trimmed via data type; if the data is Illumina or PacBio, fastp is called, otherwise it assumes the data is Oxford Nanopore then PoreChop is utilized.
- If Illumina reads are utilized, an optional bbmap step to remove the phiX174 genome is available or user provided contaminate genome. Phage phiX174 is a common contaminant within the Illumina platform as their library spike-in control. We highly recommend this removal if viral analysis is conducted, as it would provide false positives to ssDNA microviruses within a sample.
- We include a
--skip_deconoption to skip the filtration of phiX174, which may remove common k-mers that are shared in ssDNA phages. - In the formatting and gene prediction stage, contigs and genomes are checked for N repeats. These N repeats are removed by default.
- We impute contig/genome statistics (e.g., N50, N90, max contig) via our custom module Metaome Stats.
- Contigs can be converted to pORFs using Prodigal, FragGeneScanRs, and Prodigal-gv) as specified by user preference.
- Scaffold annotation is not recommended due to N's providing ambiguous annotation.
- Both Prodigal and FragGeneScanRs can be used via our
--superoption, and we recommend using FragGeneScanRs for samples rich in eukaryotes. - FragGeneScanRs found more ORFs and KOs than Prodigal for a stimulated eukaryote rich metagenome. HMMER searches against the above databases via user specified bitscore and e-values or our minimum defaults (i.e., bitscore = 25, e-value = 1 x 10-9 ).
- From any NextGen sequencing technology (from Illumina, PacBio, Oxford Nanopore)
- Type 1 raw reads (.fastq format)
- Type 2 nucleotide fasta (.fasta, .fa, .fna, .ffn format), assembled raw reads into contigs
- Type 3 protein fasta (.faa format), assembled contigs which genes are converted to amino acid sequence
- If an output directory is given, that folder will be created where all files are stored.
- If no output directory is specified, the 'results_metacerberus' subfolder will be created in the current directory.
- Gage/Pathview R analysis provided as separate scripts within R.
- We use Plotly to visualize the data
- Once the program is finished running, the html reports containing the visuals will be saved to the last step of the pipeline.
- The HTML files require plotly.js to be present. One has been provided in the package and is saved to the report folder.